Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine
About Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine
Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine is used to treat nutritional deficiencies due to various complications or long-term diseases. Nutritional deficiency occurs when the body is unable to absorb or get enough nutrients from food.
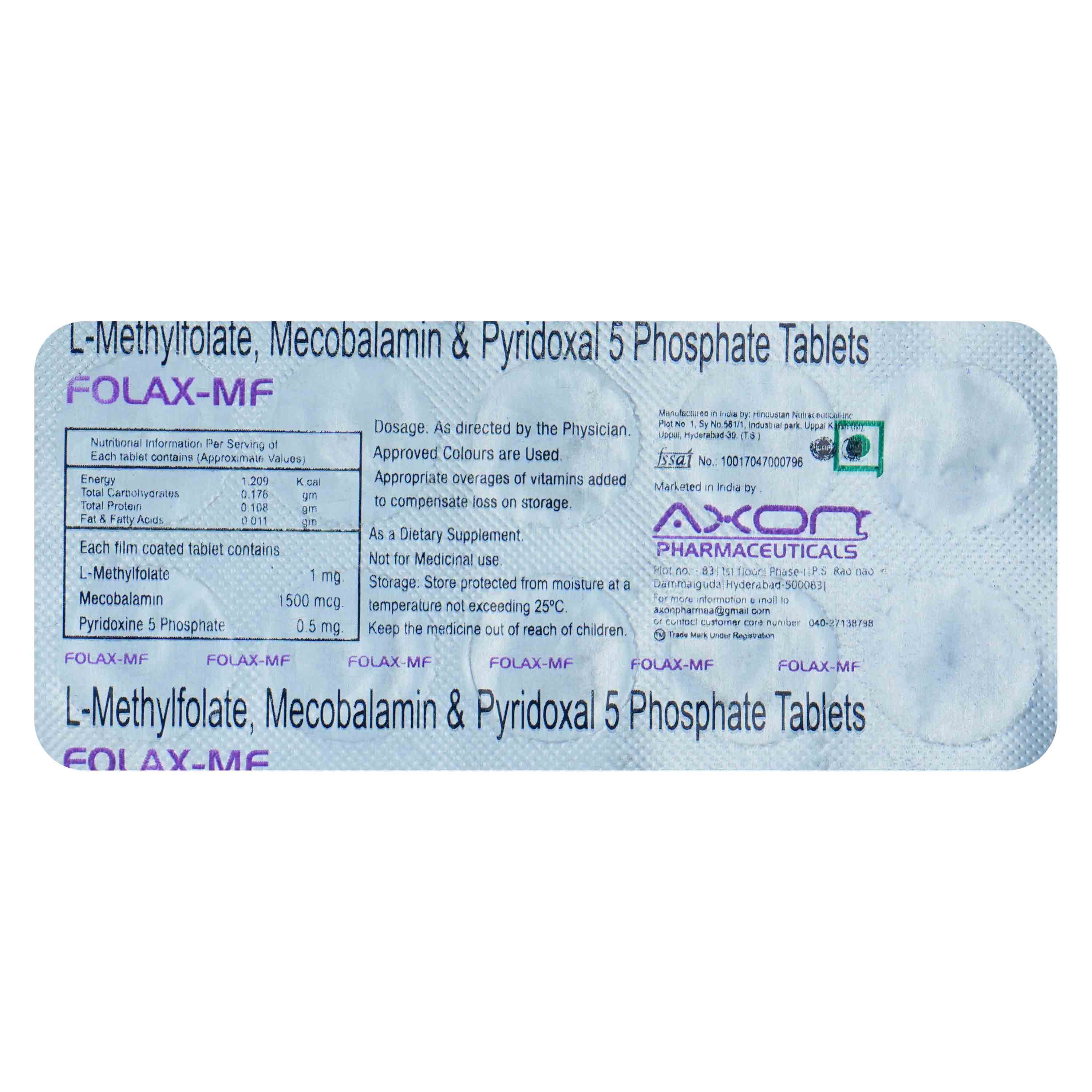
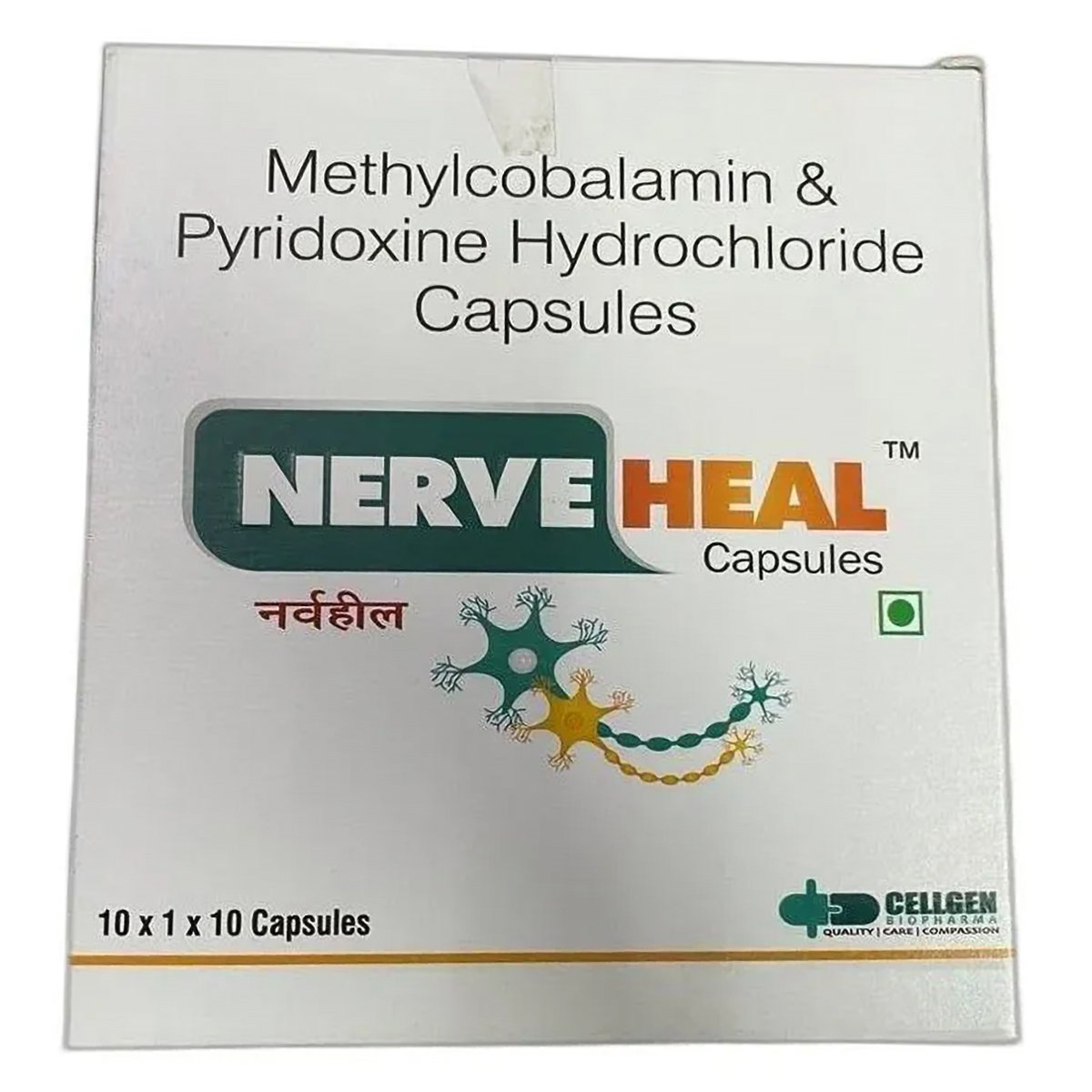
Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine contains Pyridoxine and Methylcobalamin. Pyridoxine aids metabolism and the formation of red blood cells and neurotransmitters. Methylcobalamin regulates body functions, such as cell multiplication, blood formation, and protein synthesis.
Sometimes, Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine may cause common side effects such as upset stomach, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, and dizziness. These side effects do not require medical attention and gradually resolve over time. Talk to your doctor if the side effects persist or worsen.
Let your doctor know if you use any other medications, including vitamins, before starting Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine. Please tell your doctor if you are allergic to Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine or its components. Consult your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to conceive or are a breastfeeding mother.
Uses of Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine
Medicinal Benefits
- Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine helps treat and prevent nutritional deficiencies related to vitamins B6 and B12.
- Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) supports the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates, aiding in energy production.
- It promotes the formation of red blood cells and helps prevent anaemia.
- Methylcobalamin (Vitamin B12) helps in the production of myelin, protecting and repairing nerve cells.
- It enhances overall nervous system health and improves nerve-related symptoms like tingling, numbness, or weakness.
Directions for Use
- Take Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine with or without food or as advised by a doctor.
- Follow your doctor's instructions on the dosage and timing of this medication, to ensure the safety.
- Swallow the medicine as a whole with glass of water.
- Do not crush, break, or chew it.
Storage
Side Effects of Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine
- Numbness of hands or feet
- Upset stomach
- Diarrhoea
- Loss of hunger
- Dizziness
Drug Warnings
- Let your doctor know if you have any heart, liver or kidney diseases before starting Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine.
- This supplement should be used during pregnancy only when advised by your doctor.
- Pyridoxine is excreted into breast milk. Hence, breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before taking Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine.
- Drinking alcohol may hinder Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine absorption; therefore, it is advised to limit alcohol intake while using Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine.
- Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine is safe to use in children only when advised by the doctor.
Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interaction: Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine may interact with anti-cancer drugs (altretamine, cisplatin, and arsenic trioxide), fits medicines (phenytoin, phenobarbital), antibiotics (chloramphenicol), and medicines treating Parkinson's disease (levodopa).
Drug-Food Interaction: No interaction found/established.
Drug-Disease Interaction: Use Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine with medical advice if you have malabsorption syndrome (difficulty absorbing nutrition from food), and Leber's optic atrophy.
Drug-Drug Interactions Checker List:
Safety Advice

Alcohol
cautionIt is advised to limit alcohol intake while using Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine to ensure maximum absorption of nutrients.

Pregnancy
cautionLet your doctor know if you are pregnant or planning to conceive before taking Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine.

Breast Feeding
cautionPyridoxine in Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine is excreted into the breast milk. Please consult your doctor before taking Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine if you are breastfeeding.

Driving
safeNo interactions were found/established.

Liver
consult your doctorLet your doctor know if you have any history of liver diseases before taking Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine.

Kidney
consult your doctorLet your doctor know if you have any history of kidney diseases before taking Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine.

Children
consult your doctorThe doctor will decide the dosage of Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine based on the child's age and weight.
Habit Forming
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- Try Vitamin B complex food sources like milk, cheese, eggs, liver and kidney, chicken, red meat, tuna, mackerel, and salmon, shellfish, oysters, clams, dark green vegetables, such as spinach and kale, beets, avocados, and potatoes, whole grains, cereals, kidney beans, black beans, and chickpea.
- Include fruits like citrus, banana, and watermelon in your diet.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Avoid excess fatty foods.
Special Advise
- Let your doctor and the laboratory staff know if you are using Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine since Pyridoxine may interfere with laboratory tests like the urine test for urobilinogen.
Patients Concern
Disease/Condition Glossary
Nutritional deficiency: A nutritional deficiency occurs when the body does not absorb or get enough nutrients from food. This condition occurs when a person's nutrient intake is less than the body's recommended requirement. It can lead to various health problems, such as a weak immune system, skin problems, digestive problems, defective bone growth, and neurological diseases.
FAQs
Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine is used to treat nutritional deficiencies due to various complications or long-term diseases.
Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine is a vitamin supplement that consists of pyridoxine (vitamin B6) and methylcobalamin (vitamin B12). When your body lacks these vitamins, which cannot be recovered even with food sources, Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine helps normalise these deficient levels. Collectively, Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine treats nutritional deficiencies.
Vitamin B6 deficiency occurs when your body lacks adequate Pyridoxine levels. You can overcome this deficiency by including food sources rich in Pyridoxine, like milk, eggs, beef, pork, chicken or turkey, fish, peanuts, soya beans, wheat germ, oats and bananas. If your Vitamin B6 levels are still low, your doctor may suggest its supplements.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is caused when you don't have enough methylcobalamin or Mecobalamin levels in your body. You can include natural Vitamin B12 sources like eggs, beef, liver, chicken, trout, salmon, tuna, fish, clams, fortified breakfast cereal, low-fat milk, yoghurt, and cheese in your diet to treat the deficiency. If you still have low levels of B12, please consult your doctor for its supplements.
Please do not take Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine if you are allergic to pyridoxine and Methylcobalamin, have eye problems (Leber's optic atrophy), or take levodopa for Parkinson's disease.
Pyridoxine in Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine may interfere with laboratory tests like the urine test for urobilinogen. Please make sure your doctor and the laboratory staff know that you take Methylcobalamin+pyridoxine before undergoing any blood and urine examinations.
The common signs and symptoms of low vitamin B12 include a pale yellow tinge to your skin, a sore and red tongue (glossitis), mouth ulcers, pins and needles (paraesthesia), changes in the way that you walk and move around, disturbed vision, irritability and depression.