Kafaxzim Tablet 10's



MRP ₹99
(Inclusive of all Taxes)
₹14.8 Cashback (15%)
Kafaxzim Tablet is used to treat bacterial infections. It contains Cefixime, which weakens and destroys the bacterial cell wall, leading to death. Sometimes, you may experience common side effects such as diarrhoea, nausea, loose stools, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, indigestion, and vomiting. Before taking this medicine, you should tell your doctor if you are allergic to any of its components or if you are pregnant/breastfeeding, and about all the medications you are taking and pre-existing medical conditions.
Know Your Delivery Time
Provide Delivery Location

Secure Payment

India's Most Trusted Pharmacy

Genuine Products
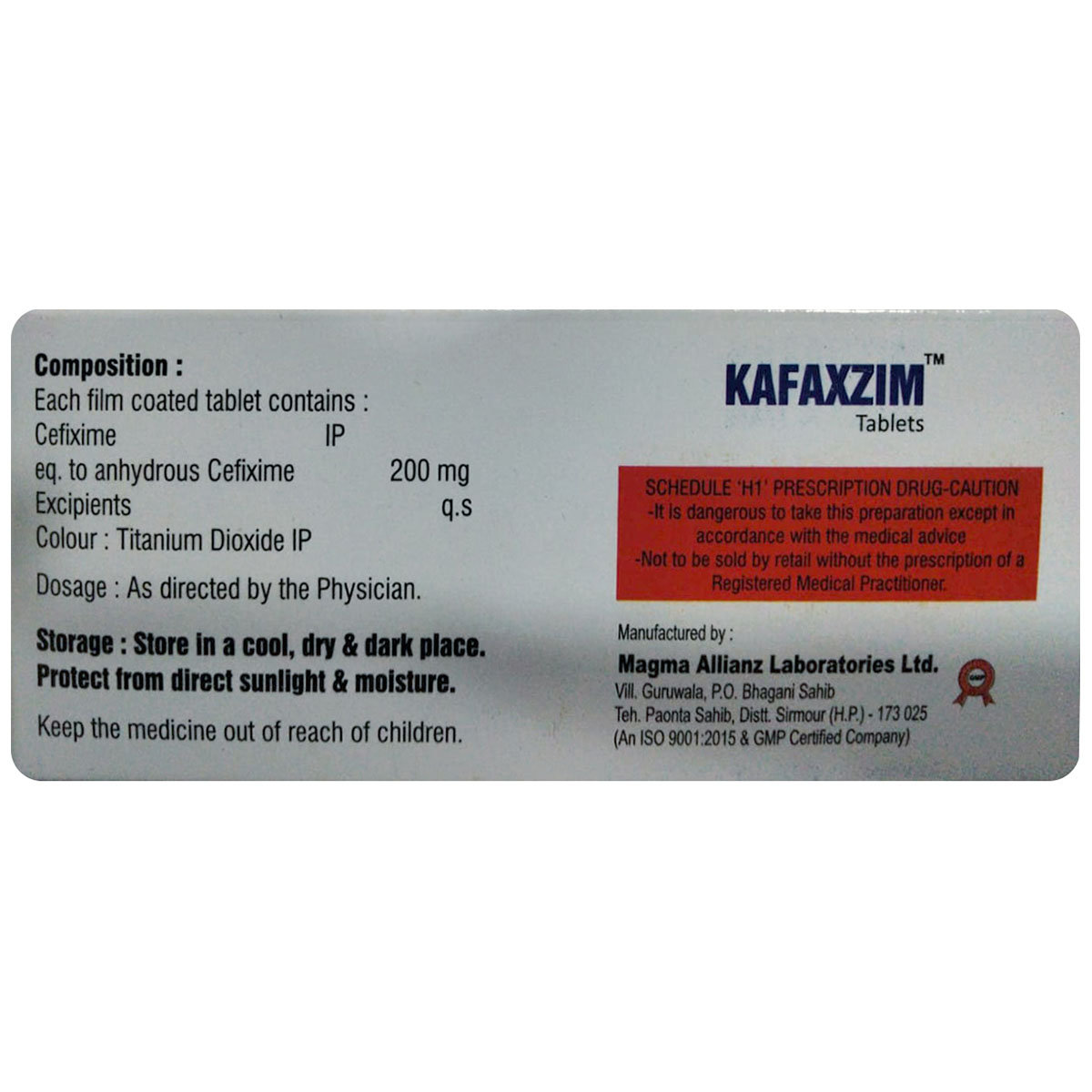
Composition :
Manufacturer/Marketer :
Consume Type :
Return Policy :
Expires on or after :
About Kafaxzim Tablet
Kafaxzim Tablet is used to treat bacterial infections of the ear, nose, sinuses (sinusitis), throat (tonsillitis, pharyngitis), chest and lungs (bronchitis, pneumonia) and urinary system (cystitis and kidney infections).
Kafaxzim Tablet contains Cefixime, which works by inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. In turn, Kafaxzim Tablet weakens and destroys the bacterial cell wall, leading to death. As a result, Kafaxzim Tablet helps to treat bacterial infections.
Sometimes, you may experience side effects such as diarrhoea, nausea, loose stools, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, indigestion, and vomiting. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and resolve gradually over time. However, talk to your doctor if you experience these side effects persistently.
Do not take Kafaxzim Tablet if you are allergic to cefixime, other cephalosporin antibiotics, or any other ingredients of this medicine. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking Kafaxzim Tablet .
Uses of Kafaxzim Tablet
Kafaxzim Tablet is used in the treatment of Bacterial Infections. The detailed uses of Kafaxzim Tablet are as follows:
- Treatment of Bacterial Infections: Kafaxzim Tablet is widely used to combat bacterial infections such as respiratory tract infections and urinary tract infections. It functions by inhibiting bacterial growth, aiding recovery.
- Management of Otitis Media: Kafaxzim Tablet may be prescribed for otitis media, a middle ear infection common in children, to alleviate pain and discomfort associated with the condition.
- Treatment of Sinusitis: Kafaxzim Tablet proves effective in treating sinusitis, which involves inflammation of the sinus cavities caused by bacterial infections. It helps relieve symptoms such as nasal congestion and pressure.
- Gonorrhea Treatment: Sometimes, Kafaxzim Tablet is used to treat gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteria. This use is usually a part of a dual therapy approach.

Have a query?
Directions for Use
- Kafaxzim Tablet can be taken with or without food or as advised by your doctor.
- Follow your doctor's instructions on the dosage and timing of this medication.
- Swallow Kafaxzim Tablet as a whole with a glass of water.
- Do not crush, break, or chew it.
Medicinal Benefits
- Kafaxzim Tablet is used to treat a wide range of bacterial infections.
- It prevents the growth of bacteria by stopping the formation of a protective covering, which is vital for its growth.
- It prevents and treats bacterial infections like ear, nose, sinuses (sinusitis), throat (tonsillitis, pharyngitis), chest and lungs (bronchitis, pneumonia) and urinary system (cystitis and kidney infections).
- Additionally, it is also prescribed to treat uncomplicated gonorrhea (cervical/urethral).
How Kafaxzim Tablet Works
Storage
- Preventing Vomiting (Before it Happens)
- Take medication exactly as prescribed by your doctor. This can help minimize side effects, including vomiting.
- Having a small meal before taking your medication can help reduce nausea and vomiting.
- Talk to your doctor about taking anti-nausea medication along with your prescribed medication.
- Managing Vomiting (If it Happens)
- Try taking ginger in the form of tea, ale, or candy to help alleviate nausea and vomiting.
- What to Do if Vomiting Persists
- Consult your doctor if vomiting continues or worsens, consult the doctor for guidance on adjusting your medication or additional treatment.
- Inform Your Doctor: Notify your doctor immediately about your diarrhoea symptoms. This allows them to adjust your medication or provide guidance on managing side effects.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to replace lost water and electrolytes. Choose water, clear broth, and electrolyte-rich drinks. Avoid carbonated or caffeinated beverages to effectively rehydrate your body.
- Follow a Bland Diet: Eat easy-to-digest foods to help firm up your stool and settle your stomach. Try incorporating bananas, rice, applesauce, toast, plain crackers, and boiled vegetables into your diet.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Steer clear of foods that can worsen diarrhoea, such as spicy, fatty, or greasy foods, high-fibre foods, and dairy products (especially if you're lactose intolerant).
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintain good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection. To stay healthy, wash your hands frequently, clean and disinfect surfaces regularly, and avoid exchanging personal belongings with others.
- Take Anti-Diarrheal Medications: If your doctor advises, anti-diarrheal medications such as loperamide might help manage diarrhoea symptoms. Always follow your doctor's directions.
- Keep track of your diarrhoea symptoms. If they don't get better or worse or are accompanied by severe stomach pain, blood, or dehydration signs (like extreme thirst or dark urine), seek medical help.
- Inform your doctor about the nausea and discuss possible alternatives to the medication or adjustments to the dosage.
- Divide your daily food intake into smaller, more frequent meals to reduce nausea.
- Opt for bland, easily digestible foods like crackers, toast, plain rice, bananas, and applesauce.
- Avoid certain foods that can trigger nausea, such as fatty, greasy, spicy, and smelly foods.
- Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broth, or electrolyte-rich beverages like coconut water or sports drinks.
- Use ginger (tea, ale, or candies) to help relieve nausea.
- Get adequate rest and also avoid strenuous activities that can worsen nausea.
- Talk to your doctor about taking anti-nausea medication if your nausea is severe.
- Record when your nausea occurs, what triggers it, and what provides relief to help you identify patterns and manage your symptoms more effectively.
- Inform Your Doctor: Notify your doctor immediately about your diarrhoea symptoms. This allows them to adjust your medication or provide guidance on managing side effects.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to replace lost water and electrolytes. Choose water, clear broth, and electrolyte-rich drinks. Avoid carbonated or caffeinated beverages to effectively rehydrate your body.
- Follow a Bland Diet: Eat easy-to-digest foods to help firm up your stool and settle your stomach. Try incorporating bananas, rice, applesauce, toast, plain crackers, and boiled vegetables into your diet.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Steer clear of foods that can worsen diarrhoea, such as spicy, fatty, or greasy foods, high-fibre foods, and dairy products (especially if you're lactose intolerant).
- Practice Good Hygiene: Maintain good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection. To stay healthy, wash your hands frequently, clean and disinfect surfaces regularly, and avoid exchanging personal belongings with others.
- Take Anti-Diarrheal Medications: If your doctor advises, anti-diarrheal medications such as loperamide might help manage diarrhoea symptoms. Always follow your doctor's directions.
- Keep track of your diarrhoea symptoms. If they don't get better or worse or are accompanied by severe stomach pain, blood, or dehydration signs (like extreme thirst or dark urine), seek medical help.
- Drink water or other clear fluids.
- To prevent worsening of pain, limit intake of tea, coffee, or alcohol.
- Include bland foods like rice, toast, crackers, and rice in your diet.
- Avoid lying down immediately after eating as it may cause indigestion or heartburn.
- Avoid acidic and spicy food as it may cause indigestion.
- Take medications with food (if recommended): It can help prevent stomach distress and indigestion.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals: Divide daily food intake into smaller, more frequent meals to ease digestion.
- Avoid trigger foods: Identify and avoid foods that trigger indigestion, such as spicy, fatty, or acidic foods.
- Stay upright after eating: Sit or stand upright for at least 1-2 hours after eating to prevent stomach acid from flowing into the oesophagus.
- Avoid carbonated drinks: Avoid drinking carbonated beverages, such as soda or beer, which can worsen indigestion.
- Manage stress: To alleviate indigestion, engage in stress-reducing activities like deep breathing exercises or meditation.
- Consult a doctor if needed: If indigestion worsens or persists, consult a healthcare professional to adjust the medication regimen or explore alternative treatments.
What if I have taken an overdose of Kafaxzim Tablet
Drug Warnings
- Do not take Kafaxzim Tablet if you are allergic to Cefixime or other cephalosporin antibiotics, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- Talk to the doctor before taking Kafaxzim Tablet if you have seizures, liver or renal dysfunction, heart disorder, or inflammation of the colon's inner lining (colitis).
- Do not take Kafaxzim Tablet without first consulting the doctor if you are pregnant, planning for pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Drive only if you are alert, as Kafaxzim Tablet may cause dizziness.
- Kafaxzim Tablet may interact with certain tests, such as those for glucose (sugar) in urine, and yield unusual results. Therefore, inform the doctor that you are using Kafaxzim Tablet before undergoing any tests.
- Do not take this medicine without consulting a healthcare professional, as self-medication may lead to antibiotic resistance, where antibiotics fail to act against specific bacterial infections.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Drug-Drug Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Co-administration of Kafaxzim Tablet with Cholera vaccine may reduce the effectiveness of the vaccine.
How to manage the interaction:
Talk to your doctor before receiving the cholera vaccine if you are currently being treated with Kafaxzim Tablet or have been treated within the last 14 days. To ensure adequate vaccine response, you should not receive cholera vaccine until at least 14 days after you complete your antibiotic therapy. Do not discontinue the medication without consulting a doctor.
Drug-Food Interactions
Drug-Food Interactions
Login/Sign Up
Diet & Lifestyle Advise
- After taking the full course of Kafaxzim Tablet , probiotics should be taken to restore some of the healthy bacteria in the intestines that may have been killed. Taking probiotics after antibiotic treatment can reduce the risk of antibiotic-associated diarrhoea. Certain fermented foods, such as yoghurt, cheese, sauerkraut, kombucha, and kimchi, can help restore the intestine's good bacteria.
- Include more fibre-enriched food in your diet, as it can be easily digested by gut bacteria, which helps stimulate their growth. Thus, fibre foods may help restore healthy gut bacteria after a course of antibiotics. Whole grains, such as whole-grain bread and brown rice, should be included in your diet.
- Avoid consuming excessive amounts of calcium, as well as iron-enriched foods and drinks, as this may interfere with the functioning of Kafaxzim Tablet .
- Avoid alcoholic beverages with Kafaxzim Tablet as it can dehydrate and affect your sleep. This can make it harder for your body to aid the Kafaxzim Tablet in fighting off infections.
Habit Forming
Therapeutic Class
All Substitutes & Brand Comparisons
RX
CEF-200 Tablet 10's
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
₹91.5
(₹7.32 per unit)
17% CHEAPERRX
Aquris Cef 200 mg Tablet 10's
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
₹102.5
(₹8.2 per unit)
7% CHEAPERRX
Cefix-200 Tablet 10's
Cipla Ltd
₹102.5
(₹8.2 per unit)
7% CHEAPER
Alcohol
Caution
It is unknown whether Kafaxzim Tablet interacts with alcohol. However, as a precautionary measure, it is advisable not to take or limit alcohol.
Pregnancy
Caution
Kafaxzim Tablet should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. Your doctor will weigh the benefits and potential risks before prescribing it. Please consult your doctor.
Breast Feeding
Unsafe
Kafaxzim Tablet should be administered to nursing mothers only if the benefits of therapy are judged to outweigh the potential risks to the infant. Hence, it is best to consult a doctor before taking Kafaxzim Tablet .
Driving
Caution
Caution should be exercised; Kafaxzim Tablet usually causes drowsiness and confusion, affecting driving ability.
Liver
Caution
Kafaxzim Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of liver diseases/conditions. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.
Kidney
Caution
Kafaxzim Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of Kidney diseases/conditions. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.
Children
Caution
Kafaxzim Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you are children below 12. Your doctor may adjust your dose depending on your age.
Heart
Please consult your doctor before using Kafaxzim Tablet if you have pre-existing heart problems. Your doctor will prescribe Kafaxzim Tablet if the benefits outweigh the risks.
Geriatrics
Consult your doctor
Please consult a doctor before administering Kafaxzim Tablet to geriatric patients. Your doctor will prescribe Kafaxzim Tablet if the benefits outweigh the risks.
FAQs
Kafaxzim Tablet is used to treat bacterial infections of the ear, nose, sinuses, throat, chest, lungs and urinary system. Additionally, it is also used to treat uncomplicated gonorrhea (cervical/urethral).
Kafaxzim Tablet comprises Cefixime. The bactericidal action of Cefixime is due to the inhibition of cell wall synthesis. In turn, Kafaxzim Tablet weakens and destroys the bacterial cell wall, ultimately leading to the cell's death. As a result, Kafaxzim Tablet helps to treat bacterial infections.
Kafaxzim Tablet can cause diarrhoea, which may be a sign of a new infection. If you have watery or bloody diarrhoea, call your doctor. Do not use anti-diarrhoea medicine unless your doctor tells you to.
If you forget to take Kafaxzim Tablet , take your dose as soon as possible. If it is almost time for the next dose, just skip that dose and take the next one when it is due. If in doubt, please contact your doctor. Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
Yes, treating urinary tract infection (UTI) by Kafaxzim Tablet may be a good alternative. However, it should be taken under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Kafaxzim Tablet is active against a very wide spectrum of bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes (the cause of strep throat), Hemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella, Shigella, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
No, it does not treat colds, flu, or other viral infections. It is intended for use only in specific bacterial infections.
Kafaxzim Tablet was effective in treating bacterial sinus infections in adults and was well tolerated.
No, it is a prescribed drug given by a physician to prevent specific medical conditions. Taking it on your own can cause unwanted side effects.
Kafaxzim Tablet may alter certain laboratory test results, like glucose (sugar) in the urine. Inform your doctor before undergoing the above test.
Talk to the doctor before taking Kafaxzim Tablet if you have seizures, liver or renal dysfunction, heart disorder, and inflammation of the colon's inner lining (colitis). Do not take Kafaxzim Tablet without first consulting the doctor if you are pregnant, planning for pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Yes, Kafaxzim Tablet is safe and effective if taken in the dose and duration prescribed by the doctor.
Kafaxzim Tablet should be taken for as long as it has been prescribed by the doctor. The doctor will determine the duration of the treatment based on your condition.
Consult a doctor if you do not experience improvement after using Kafaxzim Tablet for the prescribed duration.
If you miss a dose of Kafaxzim Tablet , take it as soon as you remember. However, if it is almost time for the scheduled dose, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the scheduled time.
Kafaxzim Tablet to be taken with caution, especially if you have a history of kidney diseases/conditions. The dose may have to be adjusted by your doctor.
Kafaxzim Tablet can be taken with or without food.
Sometimes, Kafaxzim Tablet may cause side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, loose stools, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, indigestion, and vomiting. Most of these side effects do not require medical attention and resolve gradually over time. However, you are advised to talk to your doctor if you experience these side effects persistently.
Do not discontinue Kafaxzim Tablet without consulting your doctor. To treat your condition effectively, keep taking Kafaxzim Tablet for the prescribed duration.
Country of origin
Manufacturer/Marketer address
Disclaimer
Author Details
We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and relevant information
Buy best Infections & Infestation products by
Cipla Ltd
Macleods Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Alkem Laboratories Ltd
Lupin Ltd
Abbott India Ltd
Mankind Pharma Pvt Ltd
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Micro Labs Ltd
Aristo Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Intas Pharmaceuticals Ltd
FDC Ltd
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Ipca Laboratories Ltd
Zydus Healthcare Ltd
United Biotech Pvt Ltd
Torrent Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Emcure Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Leeford Healthcare Ltd
Zuventus Healthcare Ltd
Hetero Drugs Ltd
Biochem Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd
Dr Reddy's Laboratories Ltd
Fusion Health Care Pvt Ltd
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Cadila Healthcare Ltd
Zydus Cadila
Indoco Remedies Ltd
Wockhardt Ltd
AAA Pharma Trade Pvt Ltd
Morepen Laboratories Ltd
Cadila Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Converge Biotech Pvt Ltd
GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Gufic Bioscience Ltd
Elder Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Blue Cross Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Capital Pharma
Hetero Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Alniche Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Medishri Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Akumentis Healthcare Ltd
Corona Remedies Pvt Ltd
Apex Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Pfizer Ltd
Vasu Organics Pvt Ltd
Wallace Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Veritaz Healthcare Ltd
Samarth Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Koye Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Unifaith Biotech Pvt Ltd
Laborate Pharmaceuticals India Ltd
Hegde & Hegde Pharmaceutica Llp
Overseas Health Care Pvt Ltd
Shreya Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Canixa Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
East West Pharma India Pvt Ltd
Lincoln Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Ranbaxy Laboratories Ltd
Biocon Ltd
Klm Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Natco Pharma Ltd
Zymes Bioscience Pvt Ltd
Biochemix Health Care Pvt Ltd
Medley Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Pristine Pearl Pharma Pvt Ltd
Ajanta Pharma Ltd
Allites Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Indchemie Health Specialities Pvt Ltd
Brinton Pharmaceuticals Ltd
German Remedies Ltd
J B Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Neon Laboratories Ltd
Unichem International
Yuventis Pharmaceuticals
Aurz Pharmaceutical Pvt Ltd
Unipark Biotech Pvt Ltd
Celon Laboratories Pvt Ltd
DR Johns Lab Pharma Pvt Ltd
Icarus Health Care Pvt Ltd
Kivi Labs Ltd
La Renon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Medgen Drugs And Laboratories Pvt Ltd
Megma Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Aequitas Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Aionios Pharma Pvt Ltd
BDR Pharmaceuticals Internationals Pvt Ltd
Kepler Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Indiabulls Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Suraksha Pharma Pvt Ltd
Concord Biotech Ltd
Fresenius Kabi India Pvt Ltd
Lividus Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
Nicholas Piramal India Ltd
Novartis India Ltd
Zee Laboratories Ltd
Auspharma Pvt Ltd
Biological E Ltd
Intra Life Pvt Ltd
Knoll Healthcare Pvt Ltd